Black Walnut Tree
Overview
Description
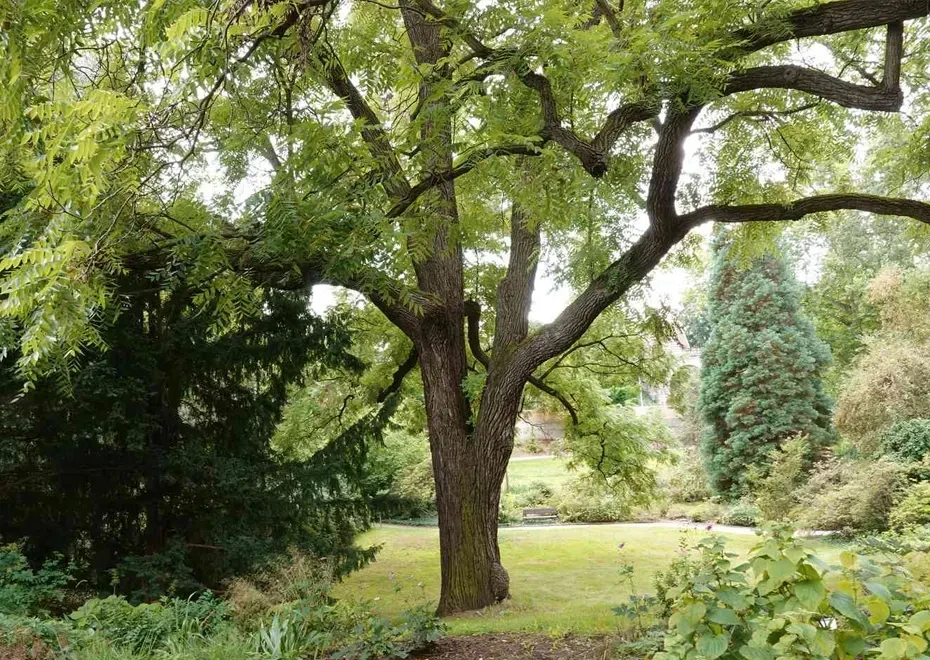
The Black Walnut tree, scientifically known as Juglans nigra, is a deciduous hardwood tree native to North America. It is a member of the Juglandaceae family and is highly valued for its timber and edible nuts.Appearance: Black Walnut trees are large and can grow to be 70-100 feet tall with a spread of 50-75 feet. They have a straight, tall trunk with a broad, rounded crown. The bark is dark brown to almost black, deeply furrowed, and develops a blocky pattern with age.
Leaves: The leaves are compound, meaning they consist of multiple leaflets. Each leaf typically has 11-23 leaflets arranged in an alternate pattern along the stem. The leaflets are lance-shaped and serrated along the edges. The foliage turns yellow in the fall before shedding for the winter.
Flowers: Black Walnut trees are monoecious, meaning they have separate male and female flowers on the same tree. The flowers are small and greenish-yellow in color. They appear in late spring or early summer before the leaves fully develop.
Nuts: The nuts produced by Black Walnut trees are highly prized for their flavor and are used in various culinary applications. The nuts are large, round, and encased in a thick, green husk that eventually darkens and splits open when ripe, revealing the hard-shelled nut inside.
Distribution: The native range of the Black Walnut tree extends from the eastern United States to parts of the Midwest and southeastern Canada. It prefers rich, well-drained soils along riverbanks and in bottomland forests.
Uses: Black Walnut wood is one of the most valuable hardwoods in North America. It is highly prized for its beautiful dark brown to purplish-black color, fine grain, and durability. The wood is commonly used in furniture making, cabinetry, gunstocks, and flooring. The nuts are harvested for consumption or processing into various products, such as baking ingredients or oils.
Challenges: While Black Walnut trees have economic and ecological value, they can also be challenging in certain situations. Their roots produce a natural herbicide called juglone, which can inhibit the growth of certain plants within their vicinity. This can make it difficult to grow certain plants under or near the tree. Additionally, the falling nuts can create a mess and may stain surfaces.
Overall, the Black Walnut tree is an important and iconic species in North American forests, contributing to both the economy and natural ecosystems. Its beautiful wood and delicious nuts make it a highly valued tree for various purposes.
Different Types of Black Walnut Tree
1. Juglans nigra (Eastern Black Walnut):
This is the most well-known and widely recognized type of Black Walnut. It is native to the eastern United States and produces large, flavorful nuts prized for their culinary use and wood prized for its quality and appearance.
2. Juglans hindsii (Hinds' Black Walnut):
Native to California and Oregon, this species is also known as the Northern California Black Walnut. It is similar to the Eastern Black Walnut but is found on the West Coast.
3. Juglans californica (Southern California Black Walnut):
Another California native, this Black Walnut species is found in the southern part of the state. It is a smaller tree compared to the Eastern Black Walnut.
4. Juglans regia (English Walnut or Persian Walnut):
Though commonly known as English or Persian Walnut, this species is also sometimes referred to as the "Common Walnut" or "European Walnut." It is native to regions in Central Asia and southeastern Europe. While closely related to Black Walnuts, it is a distinct species. English Walnuts are the most widely cultivated for commercial nut production.
5. Juglans major (Arizona Walnut):
This Black Walnut species is native to the southwestern United States and parts of Mexico. It is commonly found in Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent states.
Wood Products from Black Walnut Tree
Furniture
Black Walnut wood is highly prized for its beautiful dark brown to purplish-black color, fine grain, and durability. It is commonly used in crafting high-quality furniture pieces such as tables, chairs, cabinets, and bed frames.
Cabinetry
The rich and elegant appearance of Black Walnut wood makes it a popular choice for crafting high-end cabinetry for kitchens, bathrooms, and other living spaces. The wood's durability also ensures longevity in cabinetry construction.
Gunstocks
Black Walnut wood is used in gunstock manufacturing due to its strength, stability, and appealing aesthetics. The wood's density helps to dampen recoil and improve shooting accuracy.
Flooring
Black Walnut wood is also utilized in hardwood flooring due to its hardness and unique coloration. It adds a touch of sophistication and warmth to interior spaces.
Veneer
The attractive grain pattern of Black Walnut wood makes it suitable for creating veneer sheets. These thin slices of wood are often used to cover less expensive wood or composite materials, providing the appearance of solid Black Walnut at a more affordable cost.
Wood Crafts and Turning
Black Walnut wood is favored by woodworkers for crafting smaller items such as bowls, cutting boards, and decorative pieces. It is also popular among woodturners who create artful objects by spinning wood on a lathe.
Musical Instruments
The acoustic properties of Black Walnut wood make it a suitable material for constructing musical instruments, including guitars, violins, and other string instruments.
Benefits of Black Walnut Tree
Timber
Black Walnut wood is highly valued for its quality and appearance. It is a popular hardwood used in furniture making, cabinetry, flooring, and other high-end wood products.
Edible Nuts
The nuts produced by Black Walnut trees are not only delicious but also nutritious. They are used in various culinary applications, including baking and cooking.
Ecosystem Support
Black Walnut trees provide valuable ecosystem services. They offer shade, habitat, and food for various wildlife species, contributing to biodiversity.
Aesthetics
Black Walnut trees are known for their attractive appearance, with a straight, tall trunk and a broad, rounded crown. They add beauty and character to landscapes and urban areas.
Carbon Sequestration
Like other trees, Black Walnut trees play a role in carbon sequestration. They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it as carbon in their trunks, branches, and roots, helping mitigate the effects of climate change.
Timber Economy
The timber industry benefits from Black Walnut trees as the wood is highly sought after and valuable, supporting local economies and providing job opportunities.
Soil Stabilization
Black Walnut trees have deep and extensive root systems that help stabilize soil and prevent erosion, particularly along riverbanks and hillsides.
Natural Dye
The husks of Black Walnut nuts can be used to create a natural dye that has been historically used for staining fabrics and crafts.
Medicinal Uses
In traditional medicine, various parts of the Black Walnut tree, including the hulls, leaves, and bark, have been used for their potential medicinal properties, such as antifungal and antibacterial effects.
Cons of using Black Walnut Tree
Juglone Toxicity
Black Walnut trees produce juglone, a natural chemical that can inhibit the growth of certain plants and be toxic to some plant species. This can limit the choice of plants that can be grown near the tree.
Messy Nuts
The falling nuts from Black Walnut trees can create a mess on the ground, which may require regular cleanup, especially in areas where people walk or park vehicles.
Staining Surfaces
The husks of Black Walnut nuts contain a dark pigment that can stain surfaces such as sidewalks, driveways, and cars if they come into contact with the husks.
Slower Growth
Black Walnut trees have a relatively slow growth rate compared to some other tree species, which may mean longer wait times for the tree to reach its full size and maturity.
Potential Allergens
Some individuals may be sensitive to the pollen or other allergens produced by Black Walnut trees, which could cause allergic reactions for those with tree pollen allergies.
Root System
The extensive and aggressive root system of Black Walnut trees can compete with other nearby plants for water and nutrients, potentially impacting the growth of neighboring vegetation.
Allelopathy
In addition to juglone toxicity, Black Walnut trees may also have allelopathic effects, releasing chemicals that inhibit the growth of nearby plants and affect the diversity of plant life in the surrounding area.
Limited Range
Black Walnut trees are native to specific regions of North America and may not thrive in other climates or locations, limiting their distribution and use in certain areas.
Tips for Planting and Maintaining Black Walnut Tree
1. Choose the Right Location:
Select a planting site with full sun exposure and well-drained soil. Black Walnut trees prefer deep, fertile soils, but they can tolerate a wide range of soil types.
2. Give Adequate Space:
Black Walnut trees are large and have extensive root systems. Plant them at least 50-60 feet away from buildings and other trees to allow them enough space to grow.
3. Plant in Spring or Fall:
The best time to plant Black Walnut trees is in the spring or fall when the soil is moist and temperatures are moderate. This gives the tree time to establish its roots before extreme weather sets in.
4. Watering:
Keep the newly planted Black Walnut tree well-watered during its first year. After that, they generally don't require much additional watering, as they are drought-tolerant once established.
5. Mulching:
Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and protect the roots from temperature extremes.
6. Pruning:
Regular pruning is not necessary for Black Walnut trees, but you may want to remove any dead, damaged, or crossing branches to maintain the tree's health and shape.
7. Fertilization:
Black Walnut trees generally do not require much fertilization. However, if the soil is deficient in nutrients, a balanced fertilizer can be applied in early spring.
8. Pest and Disease Management:
Monitor the tree for pests and diseases, such as walnut caterpillars or thousand cankers disease. Contact a professional arborist if you notice any signs of issues.
9. Harvesting Nuts:
If you're planting Black Walnut trees for nut production, be prepared to harvest the nuts in the fall. Remove the husks and allow the nuts to dry thoroughly before storage.
Conclusion
Black Walnut tree (Juglans nigra) holds a position of significance and value in North American forests. Its ecological contributions are far-reaching, providing shade, shelter, and sustenance for various wildlife species. The tree's extensive root system aids in soil stabilization and erosion prevention, adding to its importance in maintaining a healthy ecosystem. Moreover, the Black Walnut's highly prized wood is sought after for its beauty, strength, and durability, making it a preferred choice for crafting high-quality furniture, cabinetry, and flooring. Additionally, the tree's nuts are a cherished culinary delight, cherished for their delicious taste and versatile use in cooking and baking. However, while the Black Walnut tree brings numerous benefits, it comes with some challenges, such as its juglone toxicity that restricts the growth of certain plants nearby and its slow growth rate that demands patience. Proper care and consideration are essential in planting and maintaining this majestic tree. Overall, the Black Walnut tree stands as a testament to the richness and diversity of nature, offering a harmonious blend of ecological significance and economic value to both nature enthusiasts and industries alike.
FAQs
1. What is a Black Walnut tree?
The Black Walnut tree (Juglans nigra) is a deciduous hardwood tree native to North America. It is known for its valuable timber and edible nuts.
2. Where are Black Walnut trees commonly found?
Black Walnut trees are native to the eastern United States and can also be found in parts of the Midwest and southeastern Canada.
3. What are the uses of Black Walnut wood?
Black Walnut wood is highly prized for its beauty and durability. It is commonly used in furniture making, cabinetry, gunstocks, flooring, and more.
4. Are Black Walnut nuts edible?
Yes, Black Walnut nuts are edible and highly valued for their delicious taste. They are used in various culinary applications, such as baking and cooking.
5. Can Black Walnut trees be grown in my garden?
Yes, Black Walnut trees can be grown in gardens and landscapes. However, keep in mind that they have an extensive root system and produce juglone, which can affect certain nearby plants.
6. How long does it take for a Black Walnut tree to mature?
Black Walnut trees have a relatively slow growth rate. It may take several decades for them to reach full maturity and their maximum height.
7. Are Black Walnut trees environmentally beneficial?
Yes, Black Walnut trees provide valuable ecosystem services. They offer shade, habitat, and food for various wildlife species, and they contribute to soil stabilization and carbon sequestration.
8. What should I consider before planting a Black Walnut tree?
Before planting a Black Walnut tree, consider its size and potential impact on the surrounding area. Be mindful of its juglone toxicity and choose a planting location accordingly. Additionally, be prepared for the slow growth rate and potential challenges of maintaining the tree.
9. Can Black Walnut trees be grown for commercial purposes?
Yes, Black Walnut trees are cultivated for their valuable timber and nuts. Commercial plantations are established for nut production and wood harvesting.
10. How do I care for a Black Walnut tree?
Proper care includes providing adequate water during the first year after planting, mulching to retain moisture, pruning as needed for health and shape, and monitoring for pests and diseases. Once established, Black Walnut trees generally require minimal maintenance.
No listings available
Related Products
Golden Jubilee Peach Tree
Prunus persica 'Golden Jubilee' is a specific cultivar of peach tree. It is a deciduous fruit tree belonging to the Rosaceae family. 'Golden Jubilee'...
Gray Dogwood
Cornus racemosa, commonly known as the gray dogwood or northern swamp dogwood, is a deciduous shrub native to eastern North America. It belongs to...
Common Fragrant Lilac
Syringa vulgaris, commonly known as the Common Lilac or French Lilac, is a deciduous shrub belonging to the genus Syringa in the olive family...
European Beech Tree
The European Beech (Fagus sylvatica) is a deciduous tree species native to much of Europe, including parts of western Asia. It is one of...
Emerald Arborvitae Tree
The Emerald Arborvitae (Thuja occidentalis 'Smaragd') is a popular evergreen tree or shrub in landscaping and gardening. It belongs to the cypress family (Cupressaceae)...
Eastern Red Cedar Tree
The Eastern Red Cedar, scientifically known as Juniperus virginiana, is a species of evergreen tree native to eastern North America. It belongs to the...
Douglas Fir Tree
The Douglas Fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) is an evergreen coniferous tree that belongs to the Pinaceae family. It is one of the most common and...
Deodar Cedar Tree
The name "Deodar" is derived from the Sanskrit words "deva" (meaning "god") and "daru" (meaning "wood" or "tree"), hence it is often referred to...
Dawn Redwood Tree
The Dawn Redwood tree, scientifically known as Metasequoia glyptostroboides, is a deciduous coniferous tree that belongs to the family Cupressaceae. It is a unique...
Colorado Blue Spruce Tree
The Colorado Blue Spruce, scientifically known as Picea pungens, is a species of coniferous tree belonging to the Pinaceae family. It is native to...