European Beech Tree
- June 21, 2023
- 0 comment

Common Name: European Beech Tree
Botanical Name: Fagus sylvatica
Family: Fagaceae
Plant Type: Deciduous tree
Lumber
European Beech lumber, scientifically known as Fagus sylvatica, is a popular hardwood species native to Europe. It is highly valued for its excellent strength, durability, and attractive appearance. The lumber is widely used in various applications, including furniture, cabinetry, flooring, and interior trim.

Mature Size and Growth Rate
The European Beech is a large tree that can reach a height of 50 to 80 feet (15 to 24 meters) at maturity, with a spread of about 40 to 60 feet (12 to 18 meters). It has a moderate growth rate, typically adding around 12 to 24 inches (30 to 60 centimeters) in height per year.

Soil Type
European Beech trees can tolerate a wide range of soil types, including clay, loam, and sandy soils. However, they thrive best in moist, well-drained soils.
Soil Preference
While European Beech trees can tolerate various soil types, they prefer soils that are rich in organic matter and have a slightly acidic to neutral pH.
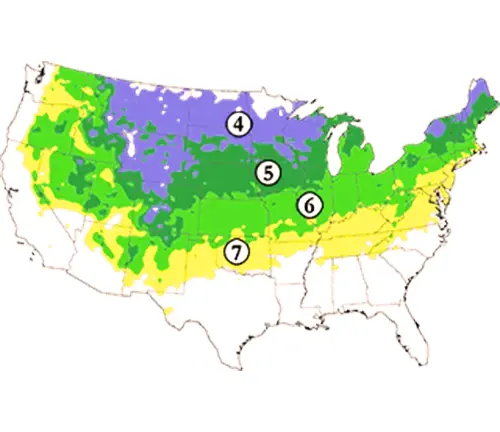
Hardiness Zones
European Beech trees are hardy in USDA Hardiness Zones 4 to 7. They are well-suited to the temperate climate of Europe, where they are native.

Sun Preference
European Beech trees can grow in full sun to partial shade. They tend to develop a more open and spreading habit in full sun, while in partial shade, they have a more upright and compact growth form.

Attributes and Characteristics
The European Beech tree is known for its stately appearance and attractive foliage. It features smooth, gray bark that develops shallow ridges and furrows with age. The leaves are oval-shaped, with a pointed tip and wavy edges, and they emerge a vibrant green in spring, turning a rich coppery bronze in autumn. The tree produces small, prickly husks that enclose beechnuts, which are a valuable food source for wildlife.
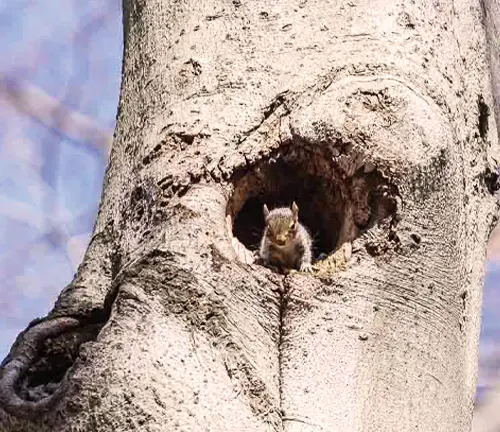

Wildlife Value
European Beech trees have significant wildlife value. The beechnuts they produce are an important food source for various animals, including birds, squirrels, and deer. The dense canopy of the tree provides shelter and nesting sites for birds, while the leaf litter on the forest floor supports a diverse range of invertebrates.

Care
To care for European Beech trees, ensure they are planted in a location with well-drained soil. Regular watering is essential, especially during dry periods. Mulching around the base of the tree helps retain soil moisture and suppress weed growth. Young trees may benefit from staking to provide support as they establish their root systems.
Benefits
European Beech trees offer numerous benefits. They provide shade and can be used for landscaping purposes due to their ornamental value. The dense foliage helps reduce noise pollution and serves as a windbreak. Additionally, these trees contribute to the overall health of ecosystems by providing habitat and food for wildlife.
Invasive
The European Beech tree is not considered invasive in its native range or in most parts of the world where it has been introduced. It is a widely cultivated and cherished species.
Lifespan
European Beech trees have a long lifespan, with some individuals living for several hundred years. It is not uncommon to find specimens that are over 300 years old.
Disadvantage
One potential disadvantage of the European Beech tree is that it can be susceptible to certain diseases, which can affect its health and longevity. It is also relatively slow-growing compared to some other tree species.

Edible or Not
The beechnuts produced by the European Beech tree are edible and have been consumed by humans for centuries. However, they have a high tannin content and are often bitter. They are mainly used as a food source for wildlife and are not commonly consumed by people.
Habitat Requirements
European Beech trees thrive in temperate climates with cool to moderate temperatures and abundant rainfall. They are typically found in mixed deciduous forests, where they form an important component of the canopy. They prefer well-drained soils but can tolerate a variety of soil types.
Name Origin
The name “Beech” is derived from the Old English word “bēce.” The botanical name, Fagus sylvatica, translates to “woodland beech” in Latin, emphasizing its natural habitat.
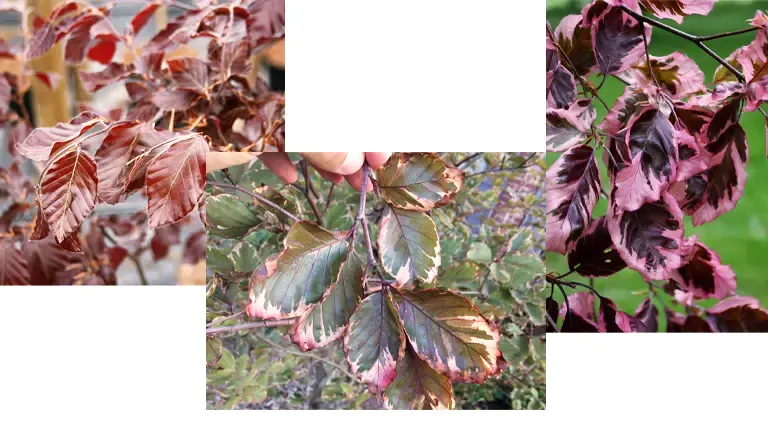

Varieties
There are several cultivated varieties of the European Beech tree, including the popular “Purpurea” variety, which has deep purple foliage, and “Tricolor,” which features variegated leaves with pink, green, and white coloration.
Pruning
Pruning European Beech trees is typically done during the dormant season to remove dead or damaged branches, improve the tree’s structure, or manage its size. It is important to be cautious when pruning, as beech trees are sensitive to excessive pruning and may respond with significant growth reduction.
Propagating
European Beech trees can be propagated through seed germination or by taking hardwood cuttings. Collect mature beechnuts in the fall and plant them immediately or store them in a cool, dry place until spring. Hardwood cuttings can be taken during the dormant season and treated with rooting hormone before planting.

Common Pests & Diseases
European Beech trees can be affected by several pests and diseases, including beech bark disease, powdery mildew, aphids, and beech-scale insects. Regular inspections, proper sanitation, and prompt treatment can help manage these issues and maintain tree health.
Fun Facts
- European Beech trees have been historically revered and associated with wisdom and knowledge.
- The wood of the European Beech is highly valued for its strength and fine grain, making it a popular choice for furniture and flooring.
- The leaves of the European Beech tree take longer to decompose than those of many other deciduous trees, contributing to the soil’s nutrient content.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can European Beech trees tolerate urban environments?
Yes, European Beech trees can tolerate urban environments as long as they have sufficient soil space, proper care, and adequate moisture. - Are European Beech trees suitable for small gardens?
European Beech trees are not recommended for small gardens due to their large size at maturity. However, smaller cultivars with more compact growth habits can be suitable for limited spaces. - Do European Beech trees attract pollinators?
While European Beech trees do produce flowers, they are wind-pollinated and do not attract pollinators in the same way as plants with showy flowers. - Can European Beech trees be used for timber?
Yes, the wood of the European Beech tree is highly valued for its strength and fine grain, making it a preferred choice for furniture, cabinetry, and flooring.
The European Beech tree stands as a majestic symbol of natural beauty and ecological importance. With its remarkable attributes and significant wildlife value, this iconic species continues to capture the admiration of tree enthusiasts and nature lovers alike.














Leave your comment