Early Harvest Apple Tree
- June 20, 2023
- 1 comment

Common Name: Early Harvest Apple Tree
Botanical Name: Malus domestica ‘Early Harvest’
Family: Rosaceae
Plant Type: Deciduous fruit tree
Lumber
The wood is light to medium in weight, with a fine to medium texture. It can range in color from light yellowish-brown to a reddish hue and often features attractive grain patterns. While apple lumber is not commonly used on a large scale due to limited availability and smaller tree size, it can be used for specialty woodworking projects, crafts, and decorative items. Its unique appearance and association with the fruit-bearing tree make it appealing to those seeking distinctive wood options.
Read more about Apple Lumber
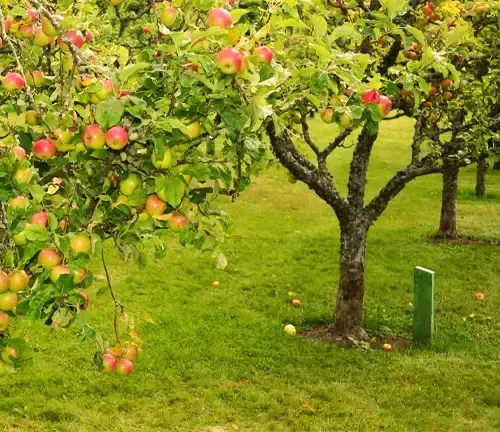

Mature Size and Growth Rate
The Early Harvest apple tree typically grows to a height of 15 to 25 feet (4.5 to 7.6 meters) and spreads about 12 to 20 feet (3.6 to 6 meters). It has a moderate growth rate.
Soil Type
Well-draining soil is preferred.
Soil Preference
The Early Harvest apple tree thrives in a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. It can tolerate a wide range of soil types, including loam, sandy, and clay soils.
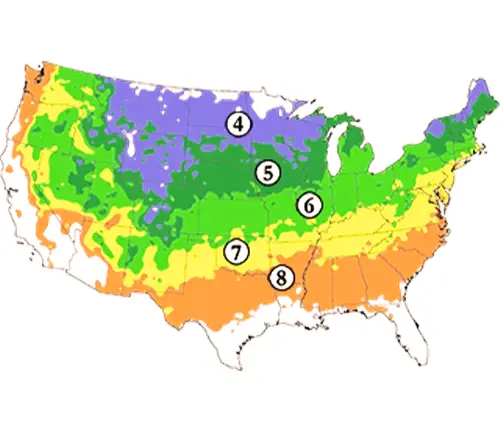
Hardiness Zones
It is hardy in USDA zones 4 to 8.
Sun Preference
The Early Harvest apple tree prefers full sun exposure, requiring at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight per day.
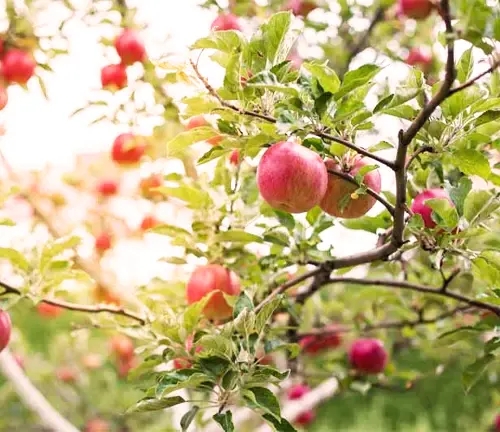

Attributes and Characteristics
The Early Harvest apple tree is known for its early ripening fruit. The apples are medium-sized with a bright yellow skin that ripens in late summer. They have a crisp, tender flesh with a mildly sweet and tangy flavor. The tree produces white blossoms in spring, adding ornamental value to the landscape. It is a self-pollinating variety but benefits from cross-pollination for increased fruit production.
Wildlife Value
The blossoms attract bees and other pollinators, aiding in the pollination process. The ripe apples provide a source of food for birds and other wildlife.

Care
The Early Harvest apple tree requires regular watering, especially during dry periods. Adequate mulching around the base of the tree helps retain moisture and control weeds. Annual pruning is essential to maintain its shape, remove dead or diseased branches, and improve air circulation. Applying organic fertilizers in early spring and late fall promotes healthy growth.
Benefits
The Early Harvest apple tree is highly valued for its early ripening fruit, allowing for an early start to the apple harvest season. The fruit can be used for fresh eating, baking, and making preserves. It is a popular choice for home orchards and small-scale fruit production.
Invasive
The Early Harvest apple tree is not considered invasive.
Lifespan
With proper care, the Early Harvest apple tree can live for 20 to 30 years or longer.
Disadvantage
One potential disadvantage of the Early Harvest apple tree is its susceptibility to certain pests and diseases, which require regular monitoring and appropriate control measures.

Edible or Not
The Early Harvest apple tree produces edible fruit that is commonly consumed.
Habitat Requirements
The Early Harvest apple tree can adapt to various soil types but thrives in well-drained soil. It prefers full sun exposure for optimal fruit production.
Name Origin
The name “Early Harvest” reflects the tree’s ability to produce fruit earlier in the growing season compared to many other apple varieties.

Varieties
Some popular Early Harvest apple tree varieties include ‘Yellow Transparent’ and ‘Primate’.
Pruning
Pruning the Early Harvest apple tree is important for maintaining its shape, removing dead or diseased branches, and promoting better fruit production. Pruning is typically done in late winter or early spring before the tree begins to bud.
Propagating
The Early Harvest apple tree can be propagated through grafting or budding techniques onto rootstock. This allows for the production of genetically identical trees with desired characteristics.
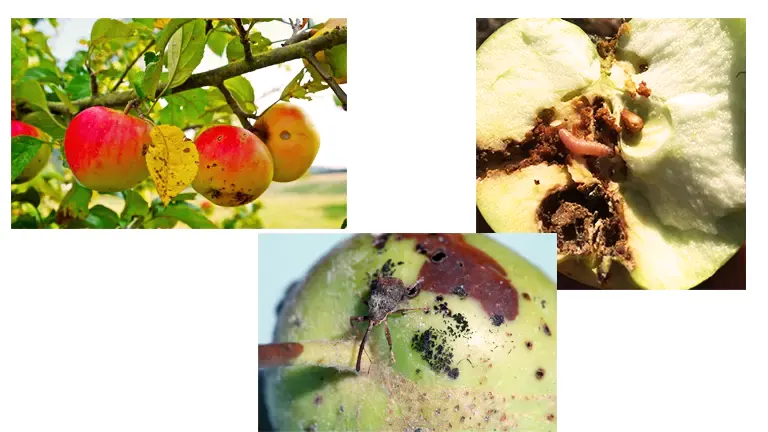

Common Pests & Diseases
Common pests that can affect the Early Harvest apple tree include apple maggots, codling moths, aphids, and spider mites. Diseases that may affect the tree include apple scab, powdery mildew, and fire blight. Regular monitoring, proper sanitation, and appropriate pest and disease management practices are essential.
Fun Facts:
- The Early Harvest apple tree is believed to have originated in the United States.
- It is one of the earliest apple varieties to ripen, usually ready for harvest in late July or early August.
- The bright yellow skin of the Early Harvest apple makes it easy to spot among the leaves of the tree.
- Early Harvest apples are often used for making applesauce and apple pies due to their excellent texture when cooked.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- Q: Can the Early Harvest apple tree self-pollinate?
A: Yes, the Early Harvest apple tree is self-pollinating, but cross-pollination with another apple tree variety can enhance fruit production. - Q: How long does it take for the Early Harvest apple tree to bear fruit?
A: The Early Harvest apple tree typically starts bearing fruit within 2 to 3 years after planting. - Q: Are Early Harvest apples good for baking?
A: Yes, Early Harvest apples are excellent for baking, as they hold their shape and provide a mildly sweet and tangy flavor to baked goods. - Q: What is the best time to harvest Early Harvest apples?
A: Early Harvest apples are best harvested when they are fully yellow and easily come off the tree with a gentle twist. - Q: Can the Early Harvest apple tree tolerate cold winters?
A: Yes, the Early Harvest apple tree is hardy in USDA zones 4 to 8 and can tolerate cold winters within this range.














make more videos about apple trees
lisa
November 1, 2023 7:24 pm